这一章,我们对WeakHashMap进行学习。 我们先对WeakHashMap有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用WeakHashMap。
目录
第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍
第2部分 WeakHashMap数据结构
第3部分 WeakHashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
第4部分 WeakHashMap遍历方式
第5部分 WeakHashMap示例
第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍
WeakHashMap简介
WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map接口。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容也是键值对(key-value)映射,而且键和值都可以是null。
不过WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。在 WeakHashMap 中,当某个键不再正常使用时,会被从WeakHashMap中被自动移除。更精确地说,对于一个给定的键,其映射的存在并不阻止垃圾回收器对该键的丢弃,这就使该键成为可终止的,被终止,然后被回收。某个键被终止时,它对应的键值对也就从映射中有效地移除了。
这个“弱键”的原理呢?大致上就是,通过WeakReference和ReferenceQueue实现的。 WeakHashMap的key是“弱键”,即是WeakReference类型的;ReferenceQueue是一个队列,它会保存被GC回收的“弱键”。实现步骤是:
(01) 新建WeakHashMap,将“键值对”添加到WeakHashMap中。
实际上,WeakHashMap是通过数组table保存Entry(键值对);每一个Entry实际上是一个单向链表,即Entry是键值对链表。
(02) 当某“弱键”不再被其它对象引用,并被GC回收时。在GC回收该“弱键”时,这个“弱键”也同时会被添加到ReferenceQueue(queue)队列中。
(03) 当下一次我们需要操作WeakHashMap时,会先同步table和queue。table中保存了全部的键值对,而queue中保存被GC回收的键值对;同步它们,就是删除table中被GC回收的键值对。
这就是“弱键”如何被自动从WeakHashMap中删除的步骤了。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap是不同步的。可以使用 Collections.synchronizedMap 方法来构造同步的 WeakHashMap。
WeakHashMap的构造函数
WeakHashMap共有4个构造函数,如下:
// 默认构造函数。
WeakHashMap()
// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity)
// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor)
// 包含“子Map”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
WeakHashMap的API
void clear()
Object clone()
boolean containsKey(Object key)
boolean containsValue(Object value)
Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet()
V get(Object key)
boolean isEmpty()
Set<K> keySet()
V put(K key, V value)
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
V remove(Object key)
int size()
Collection<V> values()
第2部分 WeakHashMap数据结构
WeakHashMap的继承关系如下
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>
↳ java.util.WeakHashMap<K, V>
WeakHashMap的声明
public class WeakHashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V> {}
WeakHashMap与Map关系如下图:
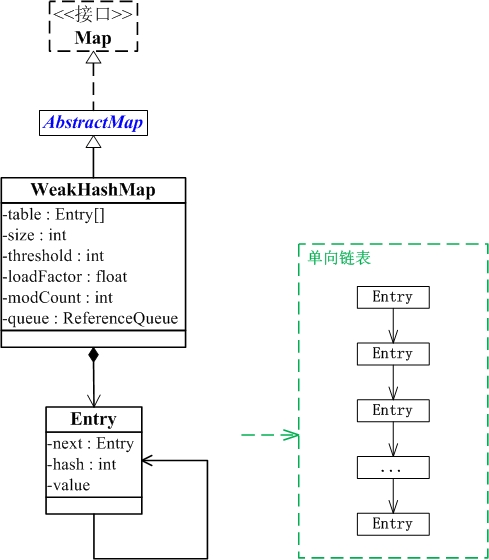
从图中可以看出:
(01) WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了Map接口。
(02) WeakHashMap是哈希表,但是它的键是"弱键"。WeakHashMap中保护几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor, modCount, queue。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的"key-value键值对"都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是Hashtable的大小,它是Hashtable保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是Hashtable的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量。threshold的值="容量*加载因子"。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的
queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
第3部分 WeakHashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
下面对WeakHashMap的源码进行说明
package java.util;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
public class WeakHashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V> {
// 默认的初始容量是16,必须是2的幂。
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
// 最大容量(必须是2的幂且小于2的30次方,传入容量过大将被这个值替换)
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认加载因子
private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 存储数据的Entry数组,长度是2的幂。
// WeakHashMap是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表
private Entry[] table;
// WeakHashMap的大小,它是WeakHashMap保存的键值对的数量
private int size;
// WeakHashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整WeakHashMap的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子)
private int threshold;
// 加载因子实际大小
private final float loadFactor;
// queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
// 弱引用和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中
private final ReferenceQueue<K> queue = new ReferenceQueue<K>();
// WeakHashMap被改变的次数
private volatile int modCount;
// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Initial Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// WeakHashMap的最大容量只能是MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load factor: "+
loadFactor);
// 找出“大于initialCapacity”的最小的2的幂
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
// 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据
table = new Entry[capacity];
// 设置“加载因子”
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 设置“WeakHashMap阈值”,当WeakHashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将WeakHashMap的容量加倍。
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
}
// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
// 默认构造函数。
public WeakHashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
}
// 包含“子Map”的构造函数
public WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, 16),
DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
// 将m中的全部元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中
putAll(m);
}
// 键为null的mask值。
// 因为WeakReference中允许“null的key”,若直接插入“null的key”,将其当作弱引用时,会被删除。
// 因此,这里对于“key为null”的清空,都统一替换为“key为NULL_KEY”,“NULL_KEY”是“静态的final常量”。
private static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();
// 对“null的key”进行特殊处理
private static Object maskNull(Object key) {
return (key == null ? NULL_KEY : key);
}
// 还原对“null的key”的特殊处理
private static <K> K unmaskNull(Object key) {
return (K) (key == NULL_KEY ? null : key);
}
// 判断“x”和“y”是否相等
static boolean eq(Object x, Object y) {
return x == y || x.equals(y);
}
// 返回索引值
// h & (length-1)保证返回值的小于length
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
// 清空table中无用键值对。原理如下:
// (01) 当WeakHashMap中某个“弱引用的key”由于没有再被引用而被GC收回时,
// 被回收的“该弱引用key”也被会被添加到"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中。
// (02) 当我们执行expungeStaleEntries时,
// 就遍历"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中的所有key
// 然后就在“WeakReference的table”中删除与“ReferenceQueue(queue)中key”对应的键值对
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry<K,V> e;
while ( (e = (Entry<K,V>) queue.poll()) != null) {
int h = e.hash;
int i = indexFor(h, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> p = prev;
while (p != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = p.next;
if (p == e) {
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.next = null; // Help GC
e.value = null; // " "
size--;
break;
}
prev = p;
p = next;
}
}
}
// 获取WeakHashMap的table(存放键值对的数组)
private Entry[] getTable() {
// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
expungeStaleEntries();
return table;
}
// 获取WeakHashMap的实际大小
public int size() {
if (size == 0)
return 0;
// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
expungeStaleEntries();
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
// 获取key对应的value
public V get(Object key) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
// 获取key的hash值。
int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
Entry[] tab = getTable();
int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);
Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
// 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素
while (e != null) {
if (e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get()))
return e.value;
e = e.next;
}
return null;
}
// WeakHashMap是否包含key
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
}
// 返回“键为key”的键值对
Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
Entry[] tab = getTable();
int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);
Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
while (e != null && !(e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get())))
e = e.next;
return e;
}
// 将“key-value”添加到WeakHashMap中
public V put(K key, V value) {
K k = (K) maskNull(key);
int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
Entry[] tab = getTable();
int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
// 若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出!
if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (value != oldValue)
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// 若“该key”对应的键值对不存在于WeakHashMap中,则将“key-value”添加到table中
modCount++;
Entry<K,V> e = tab[i];
tab[i] = new Entry<K,V>(k, value, queue, h, e);
if (++size >= threshold)
resize(tab.length * 2);
return null;
}
// 重新调整WeakHashMap的大小,newCapacity是调整后的单位
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = getTable();
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 新建一个newTable,将“旧的table”的全部元素添加到“新的newTable”中,
// 然后,将“新的newTable”赋值给“旧的table”。
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(oldTable, newTable);
table = newTable;
if (size >= threshold / 2) {
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} else {
// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
expungeStaleEntries();
transfer(newTable, oldTable);
table = oldTable;
}
}
// 将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都添加到newTable中
private void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] dest) {
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; ++j) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
src[j] = null;
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object key = e.get();
if (key == null) {
e.next = null; // Help GC
e.value = null; // " "
size--;
} else {
int i = indexFor(e.hash, dest.length);
e.next = dest[i];
dest[i] = e;
}
e = next;
}
}
}
// 将"m"的全部元素都添加到WeakHashMap中
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
return;
// 计算容量是否足够,
// 若“当前实际容量 < 需要的容量”,则将容量x2。
if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int newCapacity = table.length;
while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
newCapacity <<= 1;
if (newCapacity > table.length)
resize(newCapacity);
}
// 将“m”中的元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中。
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
// 删除“键为key”元素
public V remove(Object key) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
// 获取哈希值。
int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
Entry[] tab = getTable();
int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev;
// 删除链表中“键为key”的元素
// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
tab[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
return e.value;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return null;
}
// 删除“键值对”
Entry<K,V> removeMapping(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return null;
Entry[] tab = getTable();
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k = maskNull(entry.getKey());
int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev;
// 删除链表中的“键值对e”
// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (h == e.hash && e.equals(entry)) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
tab[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return null;
}
// 清空WeakHashMap,将所有的元素设为null
public void clear() {
while (queue.poll() != null)
;
modCount++;
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
tab[i] = null;
size = 0;
while (queue.poll() != null)
;
}
// 是否包含“值为value”的元素
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
// 若“value为null”,则调用containsNullValue()查找
if (value==null)
return containsNullValue();
// 若“value不为null”,则查找WeakHashMap中是否有值为value的节点。
Entry[] tab = getTable();
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (value.equals(e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
// 是否包含null值
private boolean containsNullValue() {
Entry[] tab = getTable();
for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (e.value==null)
return true;
return false;
}
// Entry是单向链表。
// 它是 “WeakHashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。
// 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数
private static class Entry<K,V> extends WeakReference<K> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
private V value;
private final int hash;
// 指向下一个节点
private Entry<K,V> next;
// 构造函数。
Entry(K key, V value,
ReferenceQueue<K> queue,
int hash, Entry<K,V> next) {
super(key, queue);
this.value = value;
this.hash = hash;
this.next = next;
}
public K getKey() {
return WeakHashMap.<K>unmaskNull(get());
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
// 判断两个Entry是否相等
// 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。
// 否则,返回false
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 实现hashCode()
public int hashCode() {
Object k = getKey();
Object v = getValue();
return ((k==null ? 0 : k.hashCode()) ^
(v==null ? 0 : v.hashCode()));
}
public String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}
// HashIterator是WeakHashMap迭代器的抽象出来的父类,实现了公共了函数。
// 它包含“key迭代器(KeyIterator)”、“Value迭代器(ValueIterator)”和“Entry迭代器(EntryIterator)”3个子类。
private abstract class HashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
// 当前索引
int index;
// 当前元素
Entry<K,V> entry = null;
// 上一次返回元素
Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null;
// expectedModCount用于实现fast-fail机制。
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// 下一个键(强引用)
Object nextKey = null;
// 当前键(强引用)
Object currentKey = null;
// 构造函数
HashIterator() {
index = (size() != 0 ? table.length : 0);
}
// 是否存在下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {
Entry[] t = table;
// 一个Entry就是一个单向链表
// 若该Entry的下一个节点不为空,就将next指向下一个节点;
// 否则,将next指向下一个链表(也是下一个Entry)的不为null的节点。
while (nextKey == null) {
Entry<K,V> e = entry;
int i = index;
while (e == null && i > 0)
e = t[--i];
entry = e;
index = i;
if (e == null) {
currentKey = null;
return false;
}
nextKey = e.get(); // hold on to key in strong ref
if (nextKey == null)
entry = entry.next;
}
return true;
}
// 获取下一个元素
protected Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (nextKey == null && !hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = entry;
entry = entry.next;
currentKey = nextKey;
nextKey = null;
return lastReturned;
}
// 删除当前元素
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
WeakHashMap.this.remove(currentKey);
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
currentKey = null;
}
}
// value的迭代器
private class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> {
public V next() {
return nextEntry().value;
}
}
// key的迭代器
private class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
public K next() {
return nextEntry().getKey();
}
}
// Entry的迭代器
private class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
// WeakHashMap的Entry对应的集合
private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;
// 返回“key的集合”,实际上返回一个“KeySet对象”
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet()));
}
// Key对应的集合
// KeySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的Key。
private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new KeyIterator();
}
public int size() {
return WeakHashMap.this.size();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsKey(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (containsKey(o)) {
WeakHashMap.this.remove(o);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public void clear() {
WeakHashMap.this.clear();
}
}
// 返回“value集合”,实际上返回的是一个Values对象
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs = values;
return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values()));
}
// “value集合”
// Values继承于AbstractCollection,不同于“KeySet继承于AbstractSet”,
// Values中的元素能够重复。因为不同的key可以指向相同的value。
private class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return new ValueIterator();
}
public int size() {
return WeakHashMap.this.size();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return containsValue(o);
}
public void clear() {
WeakHashMap.this.clear();
}
}
// 返回“WeakHashMap的Entry集合”
// 它实际是返回一个EntrySet对象
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;
return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
// EntrySet对应的集合
// EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的EntrySet。
private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
// 是否包含“值(o)”
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k = e.getKey();
Entry candidate = getEntry(e.getKey());
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
// 删除“值(o)”
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeMapping(o) != null;
}
// 返回WeakHashMap的大小
public int size() {
return WeakHashMap.this.size();
}
// 清空WeakHashMap
public void clear() {
WeakHashMap.this.clear();
}
// 拷贝函数。将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都拷贝到List中
private List<Map.Entry<K,V>> deepCopy() {
List<Map.Entry<K,V>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<K,V>>(size());
for (Map.Entry<K,V> e : this)
list.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<K,V>(e));
return list;
}
// 返回Entry对应的Object[]数组
public Object[] toArray() {
return deepCopy().toArray();
}
// 返回Entry对应的T[]数组(T[]我们新建数组时,定义的数组类型)
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
return deepCopy().toArray(a);
}
}
}
说明:WeakHashMap和HashMap都是通过"拉链法"实现的散列表。它们的源码绝大部分内容都一样,这里就只是对它们不同的部分就是说明。
WeakReference是“弱键”实现的哈希表。它这个“弱键”的目的就是:实现对“键值对”的动态回收。当“弱键”不再被使用到时,GC会回收它,WeakReference也会将“弱键”对应的键值对删除。
“弱键”是一个“弱引用(WeakReference)”,在Java中,WeakReference和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的。在WeakHashMap中亦是如此:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。 接着,WeakHashMap会根据“引用队列”,来删除“WeakHashMap中已被GC回收的‘弱键’对应的键值对”。
另外,理解上面思想的重点是通过 expungeStaleEntries() 函数去理解。
第4部分 WeakHashMap遍历方式
4.1 遍历WeakHashMap的键值对
第一步:根据entrySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键值对”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
// 获取key
key = (String)entry.getKey();
// 获取value
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
}
4.2 遍历WeakHashMap的键
第一步:根据keySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = (String)iter.next();
// 根据key,获取value
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
}
4.3 遍历WeakHashMap的值
第一步:根据value()获取WeakHashMap的“值”的集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer value = null;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}
WeakHashMap遍历测试程序如下:
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
* @desc 遍历WeakHashMap的测试程序。
* (01) 通过entrySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByEntryset()
* (02) 通过keySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByKeyset()
* (03) 通过values()去遍历value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapJustValues()
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class WeakHashMapIteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int val = 0;
String key = null;
Integer value = null;
Random r = new Random();
WeakHashMap map = new WeakHashMap();
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
// 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
val = r.nextInt(100);
key = String.valueOf(val);
value = r.nextInt(5);
// 添加到WeakHashMap中
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(" key:"+key+" value:"+value);
}
// 通过entrySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByEntryset(map) ;
// 通过keySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByKeyset(map) ;
// 单单遍历WeakHashMap的value
iteratorHashMapJustValues(map);
}
/*
* 通过entry set遍历WeakHashMap
* 效率高!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByEntryset(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By entryset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
key = (String)entry.getKey();
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 通过keyset来遍历WeakHashMap
* 效率低!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByKeyset(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By keyset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
key = (String)iter.next();
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 遍历WeakHashMap的values
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapJustValues(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}
}
第5部分 WeakHashMap示例
下面通过实例来学习如何使用WeakHashMap
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
import java.util.Date;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* @desc WeakHashMap测试程序
*
* @author skywang
* @email kuiwu-wang@163.com
*/
public class WeakHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testWeakHashMapAPIs();
}
private static void testWeakHashMapAPIs() {
// 初始化3个“弱键”
String w1 = new String("one");
String w2 = new String("two");
String w3 = new String("three");
// 新建WeakHashMap
Map wmap = new WeakHashMap();
// 添加键值对
wmap.put(w1, "w1");
wmap.put(w2, "w2");
wmap.put(w3, "w3");
// 打印出wmap
System.out.printf("\nwmap:%s\n",wmap );
// containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
System.out.printf("contains key two : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("two"));
System.out.printf("contains key five : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("five"));
// containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s\n",wmap.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
// remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
wmap.remove("three");
System.out.printf("wmap: %s\n",wmap );
// ---- 测试 WeakHashMap 的自动回收特性 ----
// 将w1设置null。
// 这意味着“弱键”w1再没有被其它对象引用,调用gc时会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
w1 = null;
// 内存回收。这里,会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
System.gc();
// 遍历WeakHashMap
Iterator iter = wmap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry en = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.printf("next : %s - %s\n",en.getKey(),en.getValue());
}
// 打印WeakHashMap的实际大小
System.out.printf(" after gc WeakHashMap size:%s\n", wmap.size());
}
}
运行结果:
wmap:{three=w3, one=w1, two=w2}
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
wmap: {one=w1, two=w2}
next : two - w2
after gc WeakHashMap size:1
更多内容
00. Java 集合系列目录(Category)
01. Java 集合系列01之 总体框架
02. Java 集合系列02之 Collection架构
03. Java 集合系列03之 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
04. Java 集合系列04之 fail-fast总结(通过ArrayList来说明fail-fast的原理、解决办法)
05. Java 集合系列05之 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
06. Java 集合系列06之 Vector详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
07. Java 集合系列07之 Stack详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
08. Java 集合系列08之 List总结(LinkedList, ArrayList等使用场景和性能分析)
09. Java 集合系列09之 Map架构
10. Java 集合系列10之 HashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
11. Java 集合系列11之 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
12. Java 集合系列12之 TreeMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
13. Java 集合系列13之 WeakHashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
14. Java 集合系列14之 Map总结(HashMap, Hashtable, TreeMap, WeakHashMap等使用场景)
15. Java 集合系列15之 Set架构
16. Java 集合系列16之 HashSet详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
17. Java 集合系列17之 TreeSet详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
18. Java 集合系列18之 Iterator和Enumeration比较