学完ArrayList和LinkedList之后,我们接着学习Vector。学习方式还是和之前一样,先对Vector有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码;最后再通过实例来学会使用它。
目录
第1部分 Vector介绍
第2部分 Vector数据结构
第3部分 Vector源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
第4部分 Vector遍历方式
第5部分 Vector示例
第1部分 Vector介绍
Vector简介
Vector 是矢量队列,它是JDK1.0版本添加的类。继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable这些接口。
Vector 继承了AbstractList,实现了List;所以,它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
Vector 实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在Vector中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
Vector 实现了Cloneable接口,即实现clone()函数。它能被克隆。
和ArrayList不同,Vector中的操作是线程安全的。
Vector的构造函数
Vector共有4个构造函数
// 默认构造函数
Vector()
// capacity是Vector的默认容量大小。当由于增加数据导致容量增加时,每次容量会增加一倍。
Vector(int capacity)
// capacity是Vector的默认容量大小,capacityIncrement是每次Vector容量增加时的增量值。
Vector(int capacity, int capacityIncrement)
// 创建一个包含collection的Vector
Vector(Collection<? extends E> collection)
Vector的API
synchronized boolean add(E object)
void add(int location, E object)
synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection)
synchronized boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection)
synchronized void addElement(E object)
synchronized int capacity()
void clear()
synchronized Object clone()
boolean contains(Object object)
synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized void copyInto(Object[] elements)
synchronized E elementAt(int location)
Enumeration<E> elements()
synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity)
synchronized boolean equals(Object object)
synchronized E firstElement()
E get(int location)
synchronized int hashCode()
synchronized int indexOf(Object object, int location)
int indexOf(Object object)
synchronized void insertElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized boolean isEmpty()
synchronized E lastElement()
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object, int location)
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object)
synchronized E remove(int location)
boolean remove(Object object)
synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized void removeAllElements()
synchronized boolean removeElement(Object object)
synchronized void removeElementAt(int location)
synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized E set(int location, E object)
synchronized void setElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized void setSize(int length)
synchronized int size()
synchronized List<E> subList(int start, int end)
synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
synchronized Object[] toArray()
synchronized String toString()
synchronized void trimToSize()
第2部分 Vector数据结构
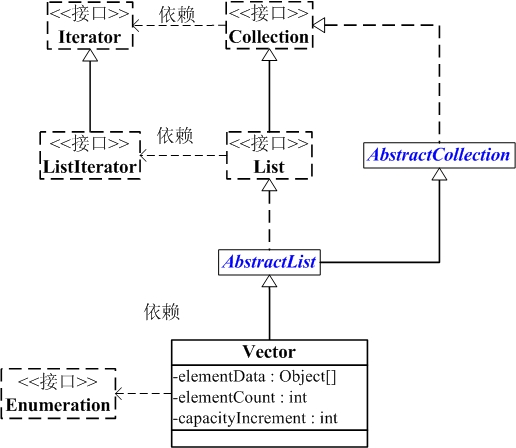
Vector的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.Vector<E>
Vector的声明
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
Vector与Collection关系如下图:
Vector的数据结构和ArrayList差不多,它包含了3个成员变量:elementData , elementCount, capacityIncrement。
(01) elementData 是"Object[]类型的数组",它保存了添加到Vector中的元素。elementData是个动态数组,如果初始化Vector时,没指定动态数组的>大小,则使用默认大小10。随着Vector中元素的增加,Vector的容量也会动态增长,capacityIncrement是与容量增长相关的增长系数,具体的增长方式,请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
(02) elementCount 是动态数组的实际大小。
(03) capacityIncrement 是动态数组的增长系数。如果在创建Vector时,指定了capacityIncrement的大小;则,每次当Vector中动态数组容量增加时>,增加的大小都是capacityIncrement。
第3部分 Vector源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
为了更了解Vector的原理,下面对Vector源码代码作出分析。
package java.util;
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 保存Vector中数据的数组
protected Object[] elementData;
// 实际数据的数量
protected int elementCount;
// 容量增长系数
protected int capacityIncrement;
// Vector的序列版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
// Vector构造函数。默认容量是10。
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
// 指定Vector容量大小的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
// 指定Vector"容量大小"和"增长系数"的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// 新建一个数组,数组容量是initialCapacity
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
// 设置容量增长系数
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
// 指定集合的Vector构造函数。
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 获取“集合(c)”的数组,并将其赋值给elementData
elementData = c.toArray();
// 设置数组长度
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
// 将数组Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组anArray中
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
// 将当前容量值设为 =实际元素个数
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
// 确认“Vector容量”的帮助函数
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 当Vector的容量不足以容纳当前的全部元素,增加容量大小。
// 若 容量增量系数>0(即capacityIncrement>0),则将容量增大当capacityIncrement
// 否则,将容量增大一倍。
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object[] oldData = elementData;
int newCapacity = (capacityIncrement > 0) ?
(oldCapacity + capacityIncrement) : (oldCapacity * 2);
if (newCapacity < minCapacity) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
// 确定Vector的容量。
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 将Vector的改变统计数+1
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
// 设置容量值为 newSize
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
// 若 "newSize 大于 Vector容量",则调整Vector的大小。
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
// 若 "newSize 小于/等于 Vector容量",则将newSize位置开始的元素都设置为null
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
// 返回“Vector的总的容量”
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
// 返回“Vector的实际大小”,即Vector中元素个数
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
// 判断Vector是否为空
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
// 返回“Vector中全部元素对应的Enumeration”
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
// 通过匿名类实现Enumeration
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
// 是否存在下一个元素
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
// 获取下一个元素
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return (E)elementData[count++];
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
// 返回Vector中是否包含对象(o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
// 从index位置开始向后查找元素(o)。
// 若找到,则返回元素的索引值;否则,返回-1
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则正向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则正向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 查找并返回元素(o)在Vector中的索引值
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
// 从后向前查找元素(o)。并返回元素的索引
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
// 从后向前查找元素(o)。开始位置是从前向后的第index个数;
// 若找到,则返回元素的“索引值”;否则,返回-1。
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则反向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则反向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 返回Vector中index位置的元素。
// 若index月结,则抛出异常
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return (E)elementData[index];
}
// 获取Vector中的第一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[0];
}
// 获取Vector中的最后一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[elementCount - 1];
}
// 设置index位置的元素值为obj
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
// 删除index位置的元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
} else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
// 在index位置处插入元素(obj)
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
// 将“元素obj”添加到Vector末尾
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
// 在Vector中查找并删除元素obj。
// 成功的话,返回true;否则,返回false。
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 删除Vector中的全部元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// 将Vector中的全部元素设为null
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
elementCount = 0;
}
// 克隆函数
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
// 将当前Vector的全部元素拷贝到v中
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
}
// 返回Object数组
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
// 返回Vector的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若数组a的大小 < Vector的元素个数;
// 则新建一个T[]数组,数组大小是“Vector的元素个数”,并将“Vector”全部拷贝到新数组中
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass());
// 若数组a的大小 >= Vector的元素个数;
// 则将Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组a中。
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount);
if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null;
return a;
}
// 获取index位置的元素
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return (E)elementData[index];
}
// 设置index位置的值为element。并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object oldValue = elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return (E)oldValue;
}
// 将“元素e”添加到Vector最后。
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
// 删除Vector中的元素o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
// 在index位置添加元素element
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
// 删除index位置的元素,并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object oldValue = elementData[index];
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return (E)oldValue;
}
// 清空Vector
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
}
// 返回Vector是否包含集合c
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
}
// 将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
// 将集合c的全部元素拷贝到数组elementData中
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 删除集合c的全部元素
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
}
// 删除“非集合c中的元素”
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
}
// 从index位置开始,将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
int numMoved = elementCount - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
// 返回两个对象是否相等
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
}
// 计算哈希值
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
// 调用父类的toString()
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
// 获取Vector中fromIndex(包括)到toIndex(不包括)的子集
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), this);
}
// 删除Vector中fromIndex到toIndex的元素
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// Let gc do its work
int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (elementCount != newElementCount)
elementData[--elementCount] = null;
}
// java.io.Serializable的写入函数
private synchronized void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
s.defaultWriteObject();
}
}
总结:
(01) Vector实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造Vecotr时;若使用默认构造函数,则Vector的默认容量大小是10。
(02) 当Vector容量不足以容纳全部元素时,Vector的容量会增加。若容量增加系数 >0,则将容量的值增加“容量增加系数”;否则,将容量大小增加一倍。
(03) Vector的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
第4部分 Vector遍历方式
Vector支持4种遍历方式。建议使用下面的第二种去遍历Vector,因为效率问题。
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}
(02) 第二种,随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。
由于Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
Integer value = null;
int size = vec.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)vec.get(i);
}
(03) 第三种,另一种for循环。
Integer value = null;
for (Integer integ:vec) {
value = integ;
}
(04) 第四种,Enumeration遍历。
Integer value = null;
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while (enu.hasMoreElements()) {
value = (Integer)enu.nextElement();
}
测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下:
import java.util.*;
/*
* @desc Vector遍历方式和效率的测试程序。
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class VectorRandomAccessTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vec= new Vector();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
vec.add(i);
iteratorThroughRandomAccess(vec) ;
iteratorThroughIterator(vec) ;
iteratorThroughFor2(vec) ;
iteratorThroughEnumeration(vec) ;
}
private static void isRandomAccessSupported(List list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
System.out.println("RandomAccess implemented!");
} else {
System.out.println("RandomAccess not implemented!");
}
}
public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
list.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRandomAccess:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughIterator:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughFor2(List list) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Object obj:list)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughFor2:" + interval+" ms");
}
public static void iteratorThroughEnumeration(Vector vec) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Enumeration enu = vec.elements(); enu.hasMoreElements(); ) {
enu.nextElement();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughEnumeration:" + interval+" ms");
}
}
运行结果:
iteratorThroughRandomAccess:6 ms
iteratorThroughIterator:9 ms
iteratorThroughFor2:8 ms
iteratorThroughEnumeration:7 ms
总结:遍历Vector,使用索引的随机访问方式最快,使用迭代器最慢。
第5部分 Vector示例
下面通过示例学习如何使用Vector
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Enumeration;
/**
* @desc Vector测试函数:遍历Vector和常用API
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class VectorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 新建Vector
Vector vec = new Vector();
// 添加元素
vec.add("1");
vec.add("2");
vec.add("3");
vec.add("4");
vec.add("5");
// 设置第一个元素为100
vec.set(0, "100");
// 将“500”插入到第3个位置
vec.add(2, "300");
System.out.println("vec:"+vec);
// (顺序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.indexOf(100):"+vec.indexOf("100"));
// (倒序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.lastIndexOf(100):"+vec.lastIndexOf("100"));
// 获取第一个元素
System.out.println("vec.firstElement():"+vec.firstElement());
// 获取第3个元素
System.out.println("vec.elementAt(2):"+vec.elementAt(2));
// 获取最后一个元素
System.out.println("vec.lastElement():"+vec.lastElement());
// 获取Vector的大小
System.out.println("size:"+vec.size());
// 获取Vector的总的容量
System.out.println("capacity:"+vec.capacity());
// 获取vector的“第2”到“第4”个元素
System.out.println("vec 2 to 4:"+vec.subList(1, 4));
// 通过Enumeration遍历Vector
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while(enu.hasMoreElements())
System.out.println("nextElement():"+enu.nextElement());
Vector retainVec = new Vector();
retainVec.add("100");
retainVec.add("300");
// 获取“vec”中包含在“retainVec中的元素”的集合
System.out.println("vec.retain():"+vec.retainAll(retainVec));
System.out.println("vec:"+vec);
// 获取vec对应的String数组
String[] arr = (String[]) vec.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.println("str:"+str);
// 清空Vector。clear()和removeAllElements()一样!
vec.clear();
// vec.removeAllElements();
// 判断Vector是否为空
System.out.println("vec.isEmpty():"+vec.isEmpty());
}
}
运行结果:
vec:[100, 2, 300, 3, 4, 5]
vec.indexOf(100):0
vec.lastIndexOf(100):0
vec.firstElement():100
vec.elementAt(2):300
vec.lastElement():5
size:6
capacity:10
vec 2 to 4:[2, 300, 3]
nextElement():100
nextElement():2
nextElement():300
nextElement():3
nextElement():4
nextElement():5
vec.retain():true
vec:[100, 300]
str:100
str:300
vec.isEmpty():true
更多内容
00. Java 集合系列目录(Category)
01. Java 集合系列01之 总体框架
02. Java 集合系列02之 Collection架构
03. Java 集合系列03之 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
04. Java 集合系列04之 fail-fast总结(通过ArrayList来说明fail-fast的原理、解决办法)
05. Java 集合系列05之 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
06. Java 集合系列06之 Vector详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
07. Java 集合系列07之 Stack详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
08. Java 集合系列08之 List总结(LinkedList, ArrayList等使用场景和性能分析)
09. Java 集合系列09之 Map架构
10. Java 集合系列10之 HashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
11. Java 集合系列11之 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
12. Java 集合系列12之 TreeMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
13. Java 集合系列13之 WeakHashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
14. Java 集合系列14之 Map总结(HashMap, Hashtable, TreeMap, WeakHashMap等使用场景)
15. Java 集合系列15之 Set架构
16. Java 集合系列16之 HashSet详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
17. Java 集合系列17之 TreeSet详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
18. Java 集合系列18之 Iterator和Enumeration比较